Difference between revisions of "Allele definition"
Farmakorakel (talk | contribs) (→Chosing the correct variants to include in the PGx alleles) |
Farmakorakel (talk | contribs) (→How to define PGx alleles for next generation sequencing) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==How to define PGx alleles for next generation sequencing== | ==How to define PGx alleles for next generation sequencing== | ||
| − | PGx alleles are defined as collections of one or more SNPs, INDELs or structural variants. When a patient is sequenced by next generation sequencing ([[NGS]]) we | + | As we saw in the previous section, PGx alleles are defined as collections of one or more SNPs, INDELs or structural variants. When a patient is sequenced by next generation sequencing ([[NGS]]) technology we typically observe more variants than those which are included in any individual PGx allele definitions. |
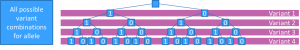
[[File:Variant tree outline.png|thumb|The 16 possible haplotypes for a four loci, decomposed variant calling]] | [[File:Variant tree outline.png|thumb|The 16 possible haplotypes for a four loci, decomposed variant calling]] | ||
This means that | This means that | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 13 September 2018
Contents
How to obtain PGx allele definitions from literature
PGx alleles are collected and distributed through various channels
- PGx alleles on JSON-LD format from the PharmGKB API
- PGx alleles on Excel-style formats, also accessible through the PharmGKB API (seems to be hidden from the Swagger documentation, but direct links when searching for haplotype definitions at the pharmgkb.org website)
- PGx alleles for use in PharmCAT are included in their source code.
- PGx alleles as VCF files from PharmVar
How to chose the correct PGx allele definitions
Chosing an appropriate genomic reference build
PGx allele definitions are given in either GRCh37 or GRCh38 reference coordinates. PharmCAT, CPIC and PharmGKB as a rule use build GRCh38. The process of changing from GRCh37 to GRCh38 for the PharmGKB API seems to be only partially completed. For instance, in the PharmGKB API JSON-LD data, the build is given as "hg38", but the actual coordinates are mostly GRCh37 (hg19). In the PharmGKB and CPIC Excel sheets, the move to GRCh38 is completed.
Chosing the correct variants to include in the PGx alleles
The allele definitions from PharmGKB and PharmVar are not always one-to-one, and some background knowledge about why this is, is required. Prefiltering of PharmGKB allele definitions was performed by the PGx pipeline of the University of Tartu, although the exact prefiltering was not published in the supplementary material to Reisberg et al..
Take as an example that illustrates many of these problems CYP2C19*19:
| CYP2C19*19 | PharmGKB | PharmVar | PharmCAT | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC_000010.10(GRCh37) | g.96522561T(rs17885098), g.96602623G(rs3758581), g.96522613A>G, g.96609568T>C(rs4917623) | g.96521422A>G(rs7902257), g.96522613A>G | g.96522613A>G(by liftOver) | Disagree on rs4917623(intron), rs7902257(2kb upstream variant). Disagree on requirement that rs17885098 and rs3758581 must be reference (i.e. only PharmGKB require that these coordinates are not missing). The reason that PharmGKB has included these positions is that they assume different reference bases for these positions (seems like a problem caused by change of Major allele between reference builds GRCh37/GRCh38, which is inverted in PharmGKB vs dbSNP and LiftOver) |
| NC_000010.11(GRCh38) | g.94762856A>G | g.94762804C>T(rs17885098), g.94762856A>G, g.94842866A>G(rs3758581) | g.94762856A>G | PharmGKB does not agree with itself when reporting GRCh38 variants in Excel sheets and GRCh37 variants in the API. The differences probably caused by non-standard use of Major/Minor Allele (rs17885098, rs3758581) with respect to dbSNP. Filtering out intron variants (rs4917623) in the Excel sheet may be sensible from an exon/protein-coding view. |
The main problem with the changes in definitions is that the same patient may be given different PGx-advice depending on the build version of the pipeline (unless of course that the haplotype is always conserved)
How to define PGx alleles for next generation sequencing
As we saw in the previous section, PGx alleles are defined as collections of one or more SNPs, INDELs or structural variants. When a patient is sequenced by next generation sequencing (NGS) technology we typically observe more variants than those which are included in any individual PGx allele definitions.
This means that
- Patients may have a large, ambiguous number of matching PGx alleles
- Patients may have additional variants that may modify the effect of a known PGx allele
We illustrate some of the problems that we encountered when trying to match patient haplotypes to the PGx allele definitions, by a four loci PGx gene
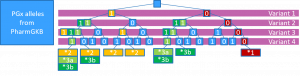
The SNP array method
This definition only requires matches for variants explicitly included in PGx allele definitions.
This means that
- Several PGx alleles may match the patient
- But the presence of additional variants will have no effect on reported PGx alleles
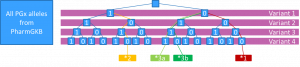
The PharmCAT method
This definition requires matches also for variants not explicitly included in PGx allele definitions.
This means that
- Only one PGx allele can exist simultaneously for the same patient
- But whenever we have additional variants, no PGx alleles will be reported
(Note that in practice PharmCAT lets the user decide which allele definitions to use in their NamedAlleleMatcher)
Which definition should we stick to?
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| SNP array method | Compatible with previous SNP array methods. Assigns PGx alleles to the maximum number of patients | Multiple PGx alleles are possible |
| PharmCAT method | One PGx allele per patient | Less compatible with previous SNP array methods. Some patients are no longer assigned to a known PGx allele |